Industrial automation plays a vital role in modern manufacturing, enabling businesses to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and ensure consistent product quality. One of the key components in industrial automation is the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), and Siemens, a global leader in automation technology, offers a wide range of PLC solutions for various industries. If you're a beginner eager to dive into the world of Siemens PLC programming, this article will provide you with a foundational understanding of the subject.
What is a PLC?
A PLC, or Programmable Logic Controller, is a digital computer used to automate electromechanical processes in industries such as manufacturing, energy, automotive, and more. PLCs are designed to endure harsh industrial environments and are responsible for controlling a wide array of machines and processes.
Why Siemens PLC?
Siemens has established itself as a leading provider of PLC systems due to its reliability, versatility, and comprehensive range of offerings. Siemens PLCs come equipped with user-friendly programming software, efficient hardware, and extensive support, making them an excellent choice for beginners and experienced programmers alike.
Getting Started with Siemens PLC Programming
- Understand PLC Basics: Before diving into Siemens PLC programming, grasp the fundamental concepts of PLC operation. This includes understanding digital and analog inputs/outputs, ladder logic, timers, counters, and data registers. These elements form the foundation of any PLC program.
- Selecting the Right Siemens PLC: Siemens offers a wide range of PLCs catering to different requirements. Depending on the scale and complexity of your application, choose an appropriate PLC model that suits your needs.
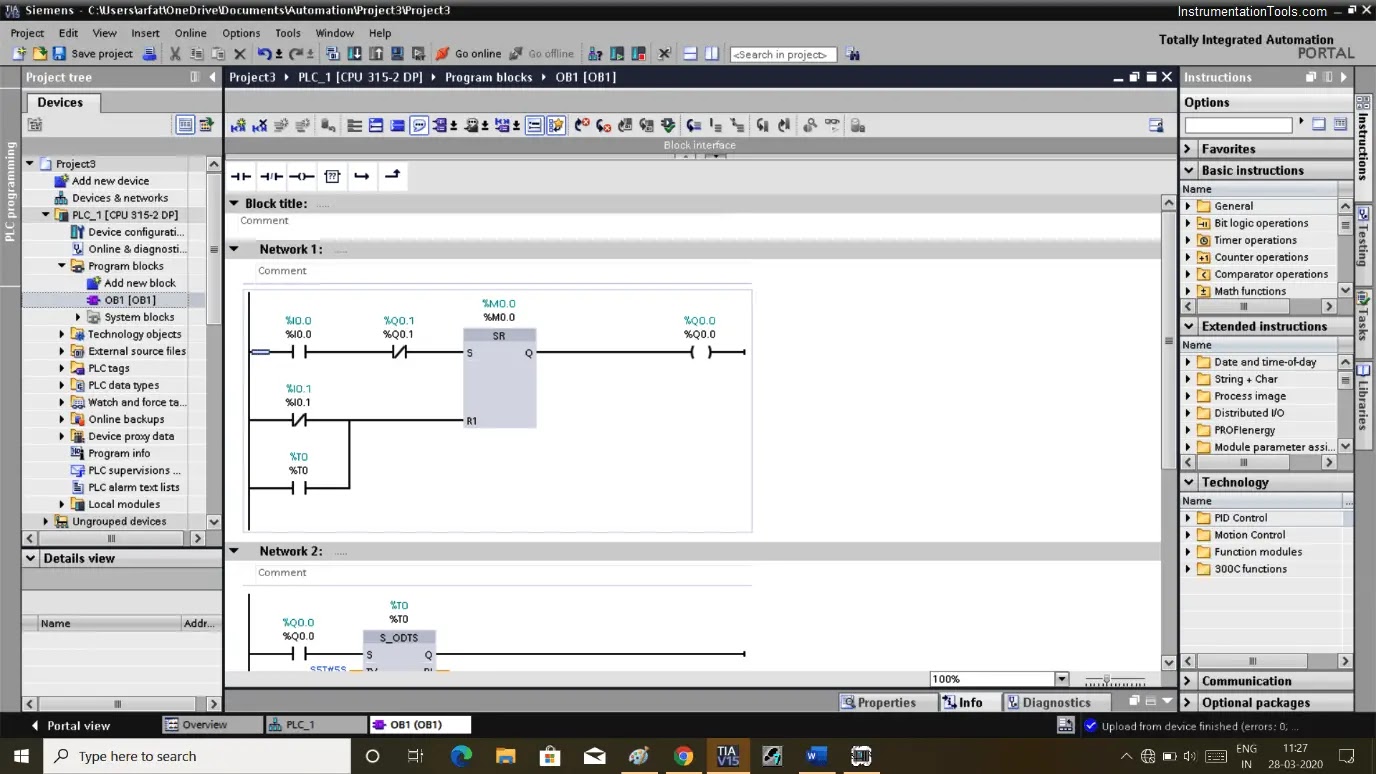
- Step 7 TIA Portal: Step 7 TIA (Totally Integrated Automation) Portal is Siemens' programming software used to develop PLC programs. It provides an integrated environment for PLC programming, HMI (Human-Machine Interface) design, and other automation tasks. Install the TIA Portal and get familiar with its interface.
- Creating a New Project: Once the software is installed, start by creating a new project for your PLC. Select the appropriate PLC model and hardware configuration. The TIA Portal will provide a graphical representation of the PLC, its modules, and I/O connections.
- Understanding Ladder Logic: Ladder Logic is the most common programming language used in PLCs. It represents logic operations through graphical diagrams resembling electrical relay circuits. Learn the basics of ladder logic, such as contacts, coils, and rungs.
- Programming Logic: Start building your PLC program by implementing the logic required to control your application. Begin with simple operations and gradually increase the complexity as you gain confidence.
- Testing and Simulation: TIA Portal allows you to test and simulate your PLC program without connecting to actual hardware. Use this feature to identify errors, fine-tune the logic, and ensure the program functions as intended.
- Uploading and Downloading: Once your program is thoroughly tested, upload it to the physical PLC via TIA Portal. Remember to take appropriate precautions during this process to avoid any disruption to the running industrial process.
Learning Resources and Support
Siemens provides extensive learning resources for PLC programming beginners. Their official website offers tutorials, manuals, and documentation to help you get started. Additionally, you can find online forums, community discussions, and video tutorials created by experienced PLC programmers.
Safety Considerations
When working with industrial equipment and PLCs, safety should be a top priority. Ensure you have a good understanding of the machinery you are controlling and follow safety guidelines to prevent accidents and injuries.
Download
Conclusion
Siemens PLC programming opens the door to a fascinating world of industrial automation. With the right foundation of knowledge and dedication to learning, beginners can quickly grasp the concepts and start developing practical PLC applications. Remember that practice, experimentation, and a willingness to learn from mistakes are key to becoming proficient in Siemens PLC programming. So, roll up your sleeves, immerse yourself in the automation world, and let Siemens PLCs power your journey to efficiency and productivity in the industrial landscape.